The connection between what we eat and how we feel extends far beyond physical health. Recent research has begun to uncover fascinating links between vegetarian diets and improved mental well-being. As more people adopt plant-based lifestyles, scientists are discovering that the benefits may reach far beyond the physical aspects of health, potentially offering significant advantages for mental health.
The Science Behind the Connection

The relationship between vegetarian diets and mental health is rooted in complex biochemical interactions. Plant-based foods are rich in essential nutrients that play crucial roles in brain function and emotional regulation. For instance, fruits and vegetables contain high levels of antioxidants that help reduce inflammation in the body, including the brain. This anti-inflammatory effect may help protect against depression and anxiety, conditions that have been linked to chronic inflammation.
Serotonin Production and Plant-Based Eating
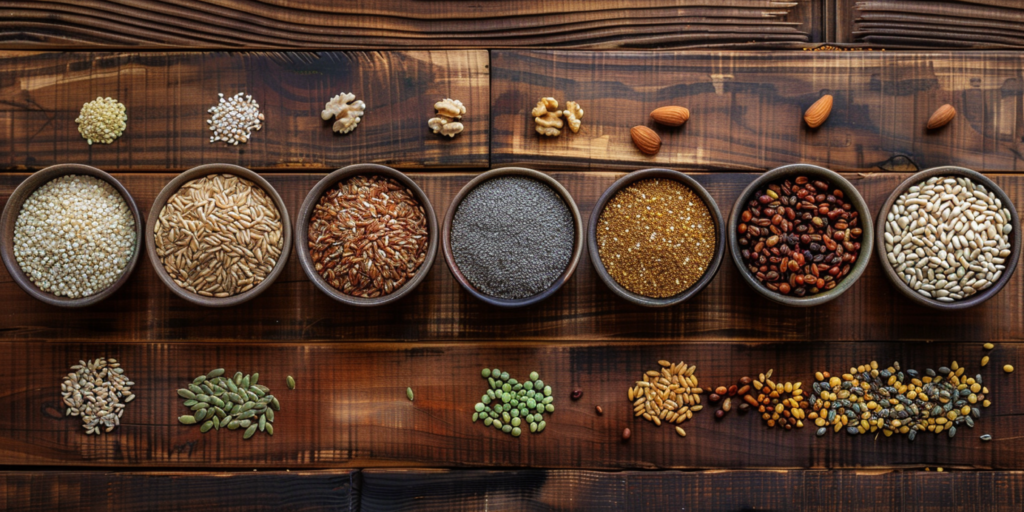

One of the most significant ways vegetarian diets may influence mental health is through their impact on serotonin production. Many plant-based foods are rich in tryptophan, an amino acid necessary for producing serotonin, often called the “happiness hormone.” Whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds provide steady sources of this essential compound, potentially supporting more stable mood regulation.
Gut-Brain Connection
The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in mental health, and vegetarian diets tend to support a diverse and healthy gut bacteria population. The high fiber content in plant-based foods feeds beneficial gut bacteria, which produce neurotransmitters that affect mood and cognitive function. This gut-brain axis is increasingly recognized as a key factor in mental well-being.

Reduced Environmental Anxiety

Many people report feeling a sense of emotional relief and reduced anxiety after adopting a vegetarian diet, particularly related to environmental concerns. Knowing that their dietary choices align with their environmental values can lead to improved mental well-being and a greater sense of purpose. This alignment between actions and values often contributes to better psychological health.
Social Connection and Community

The vegetarian community often provides strong social support networks, which are crucial for mental health. Sharing recipes, attending vegetarian events, and connecting with like-minded individuals can create a sense of belonging and purpose. These social connections can help combat feelings of isolation and contribute to better mental health outcomes.
Nutrient Density and Brain Health

Vegetarian diets typically include a wide variety of nutrient-dense foods that support brain health. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, zinc, and magnesium are abundant in well-planned vegetarian diets. These nutrients play essential roles in cognitive function, mood regulation, and stress management.
Impact on Sleep Quality

Many vegetarians report improved sleep quality, which has direct implications for mental health. Plant-based diets tend to be rich in nutrients that support healthy sleep patterns, such as magnesium and complex carbohydrates. Better sleep naturally leads to improved mood, reduced anxiety, and better cognitive function.
Stress Response and Inflammation

Research suggests that plant-based diets may help improve the body’s stress response. The high antioxidant content of vegetarian diets helps combat oxidative stress, which can affect both physical and mental health. Lower levels of inflammation may lead to reduced risk of anxiety and depression.
Weight Management and Self-Image

Vegetarian diets often support healthy weight management, which can positively impact self-image and mental well-being. The relationship between body image and mental health is well-documented, and maintaining a healthy weight through plant-based eating can contribute to improved self-esteem and reduced anxiety about weight-related health issues.
Mindful Eating Practices
Adopting a vegetarian diet often leads to more mindful eating practices. This increased awareness of food choices and their impact can extend to other areas of life, promoting mindfulness and better mental health overall. Mindful eating has been linked to reduced stress and anxiety around food.
Making the Transition
For those considering a vegetarian diet for mental health benefits, it’s important to approach the transition thoughtfully. Start gradually, ensure proper nutrient intake, and consider consulting with healthcare providers. Pay attention to how dietary changes affect your mood and energy levels, and make adjustments as needed.
Supporting Mental Health Through Diet
To maximize the mental health benefits of a vegetarian diet, focus on:
- Including a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables
- Consuming adequate protein from plant sources
- Ensuring sufficient B12 intake through fortified foods or supplements
- Incorporating healthy fats from sources like nuts, seeds, and avocados
- Maintaining regular meal times and staying hydrated
While dietary changes can significantly impact mental health, they should not replace professional mental health care when needed. A vegetarian diet can be part of a comprehensive approach to mental well-being that may include therapy, medication, exercise, and other lifestyle factors.
Research into the connection between vegetarian diets and mental health continues to evolve. As we learn more about the complex relationships between diet and mental well-being, we may discover even more ways that plant-based eating supports psychological health.

The link between vegetarianism and improved mental health is multifaceted, involving biological, psychological, and social factors. While everyone’s experience is unique, the growing body of evidence suggests that a well-planned vegetarian diet can be a valuable tool in supporting mental well-being. As with any significant lifestyle change, it’s important to approach vegetarianism mindfully and ensure that your dietary choices support your overall health goals, both mental and physical.